100 lines
5.8 KiB
Markdown
100 lines
5.8 KiB
Markdown
|
|
- [Overview](#overview)
|
||
|
|
- [Phabricator integration](#phabricator-integration)
|
||
|
|
- [Buildkite pipelines](#buildkite-pipelines)
|
||
|
|
- [Life of pre-merge check](#life-of-pre-merge-check)
|
||
|
|
- [Enabled projects and project detection](#enabled-projects-and-project-detection)
|
||
|
|
- [Agent machines](#agent-machines)
|
||
|
|
- [Compilation caching](#compilation-caching)
|
||
|
|
- [Buildkite monitoring](#buildkite-monitoring)
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
<small><i><a href='http://ecotrust-canada.github.io/markdown-toc/'>Table of contents generated with markdown-toc</a></i></small>
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# Overview
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
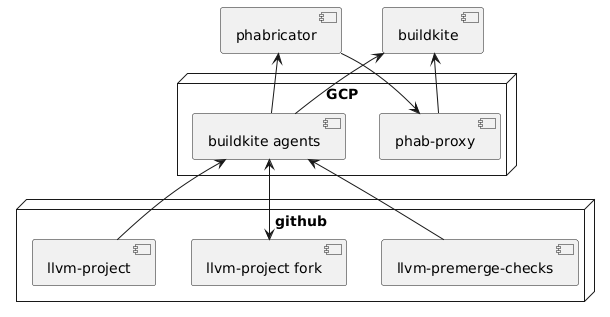
* [Buildkite](https://buildkite.com/llvm-project) orchestrates each build.
|
||
|
|
* multiple Linux and windows agents connected to Buildkite. Agents are run at Google Cloud Platform.
|
||
|
|
* [small proxy service](/phabricator-proxy) that takes build requests from [reviews.llvm.org](http://reviews.llvm.org) and converts them into Buildkite build request. Buildkite job sends build results directly to Phabricator.
|
||
|
|
* every review creates a new branch in [fork of llvm-project](https://github.com/llvm-premerge-tests/llvm-project).
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# Phabricator integration
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
* [Harbormaster build plan](https://reviews.llvm.org/harbormaster/plan/5On the Phabricator side these things were configured:/)
|
||
|
|
* Herald [rule for everyone](https://reviews.llvm.org/H576) and for [beta testers](https://reviews.llvm.org/H511).
|
||
|
|
Note that right now there is no difference between beta and "normal" builds.
|
||
|
|
* the [merge_guards_bot user](https://reviews.llvm.org/p/merge_guards_bot/) account for writing comments.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# Buildkite pipelines
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Buildkite allows [dynamically define pipelines as the output of a command](https://buildkite.com/docs/pipelines/defining-steps#dynamic-pipelines).
|
||
|
|
That gives us the flexibility to generate pipeline code using a script from a specific branch of pre-merge checks.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
For example, "pre-merge" pipeline has a single fixed step, that checks out this repo and runs a python script to
|
||
|
|
generate further steps:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
```shell script
|
||
|
|
export SRC=${BUILDKITE_BUILD_PATH}/llvm-premerge-checks
|
||
|
|
rm -rf ${SRC}
|
||
|
|
git clone --depth 1 --branch ${scripts_branch:-master} https://github.com/google/llvm-premerge-checks.git ${SRC}
|
||
|
|
export SCRIPT_DIR=${SRC}/scripts
|
||
|
|
${SCRIPT_DIR}/buildkite/build_branch_pipeline.py | tee /dev/tty | buildkite-agent pipeline upload
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
One typically edits corresponding script, not a pipeline definition in the Buildkite interface. [How to test changes](playbooks.md#testing-changes-before-merging).
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# Life of pre-merge check
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
When new diff arrives for review it triggers Herald rule ("everyone" or "beta testers").
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
That in sends an HTTP POST request to [**phab-proxy**](../phabricator-proxy) that submits a new buildkite job **diff-checks**.
|
||
|
|
All parameters from the original request are put in the build's environment with `ph_` prefix (to avoid shadowing any Buildkite environment variable).
|
||
|
|
"scripts_branch" parameter defines which branch of llvm-premerge-checks to use.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
**diff-checks** pipeline ([create_branch_pipeline.py](../scripts/buildkite/create_branch_pipeline.py)) downloads a patch (or series of patches) and applies it to a fork of the llvm-project repository.
|
||
|
|
Then it pushes a new state as a new branch (e.g. "phab-diff-288211") and triggers "premerge-checks" on it (all "ph_" env variables are passed to it).
|
||
|
|
This new branch can now be used to reproduce the build or by another tooling.
|
||
|
|
Periodical **cleanup-branches** pipeline deletes branches older than 30 days.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
**premerge-checks** pipeline ([build_branch_pipeline.py](../scripts/buildkite/build_branch_pipeline.py)) builds and tests
|
||
|
|
changes on Linux and Windows agents. Then it uploads a combined result to Phabricator.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# Enabled projects and project detection
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
To reduce build times and mask unrelated problems, we're only building and testing the projects that were modified by a patch.
|
||
|
|
[choose_projects.py](../scripts/choose_projects.py) uses manually maintained [config file](../scripts/llvm-dependencies.yaml) to define inter-project dependencies and exclude projects:
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
1. Get prefix (e.g. "llvm", "clang") of all paths modified by a patch.
|
||
|
|
1. Add all dependant projects.
|
||
|
|
1. Add all projects that this extended list depends on, completing the dependency subtree.
|
||
|
|
1. Remove all disabled projects.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# Agent machines
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
All build machines are running from Docker containers so that they can be debugged, updated, and scaled easily:
|
||
|
|
* [Linux](../containers/buildkite-premerge-debian/Dockerfile).
|
||
|
|
We use [Kubernetes deployemnt](../kubernetes/buildkite) to manage these agents.
|
||
|
|
* [Windows](../containers/agent-windows-buildkite/Dockerfile) based on [Windows vs2019](../containers/agent-windows-vs2019).
|
||
|
|
At the moment they are run as multiple individual VM instances.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
See [playbooks](playbooks.md) how to manage and set up machines.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# Compilation caching
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
Each build is performed on a clean copy of the git repository. To speed up the builds [ccache](https://ccache.dev/) is used on Linux and [sccache](https://github.com/mozilla/sccache) on Windows.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
# Buildkite monitoring
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
VM instance `buildkite-monitoring` exposes Buildkite metrics to GCP.
|
||
|
|
To set up a new instance:
|
||
|
|
1. Create as small Linux VM with full access to *Stackdriver Monitoring API*.
|
||
|
|
2. Follow instructions to [install monitoring agent](https://cloud.google.com/monitoring/agent/install-agent) and [enable statsd plugin](https://cloud.google.com/monitoring/agent/plugins/statsd).
|
||
|
|
3. Download recent release of [buildkite-agent-metrics](https://github.com/buildkite/buildkite-agent-metrics/releases).
|
||
|
|
4. Run in SSH session:
|
||
|
|
```bash
|
||
|
|
chmod +x buildkite-agent-metrics-linux-amd64
|
||
|
|
nohup ./buildkite-agent-metrics-linux-amd64 -token XXXX -interval 30s -backend statsd &
|
||
|
|
```
|
||
|
|
.
|
||
|
|
|
||
|
|
TODO: update "Testing scripts locally" playbook on how to run Linux build locally with Docker.
|